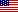
Bearings

Ball Bearings & Roller Bearings
We at, MDM Bearings Inc, stocks more than 180,000 unique bearing sizes of every major brand and type including: Ball Bearings, Roller Bearings, Spherical Roller Bearings, Cylindrical Roller Bearings, Tapered Roller Bearings, Pillow Blocks, Flange Units, and Needle Bearings, among others.
We work directly with manufacturers as distributors of bearings, we can always ensure you that we will have the technical know-how to make sure your order exactly what you need with no surprises. Every part we sell is carefully inspected for accuracy and quality. Whether in original boxes or our packaging, you can be confident that the products you receive meet your satisfaction.

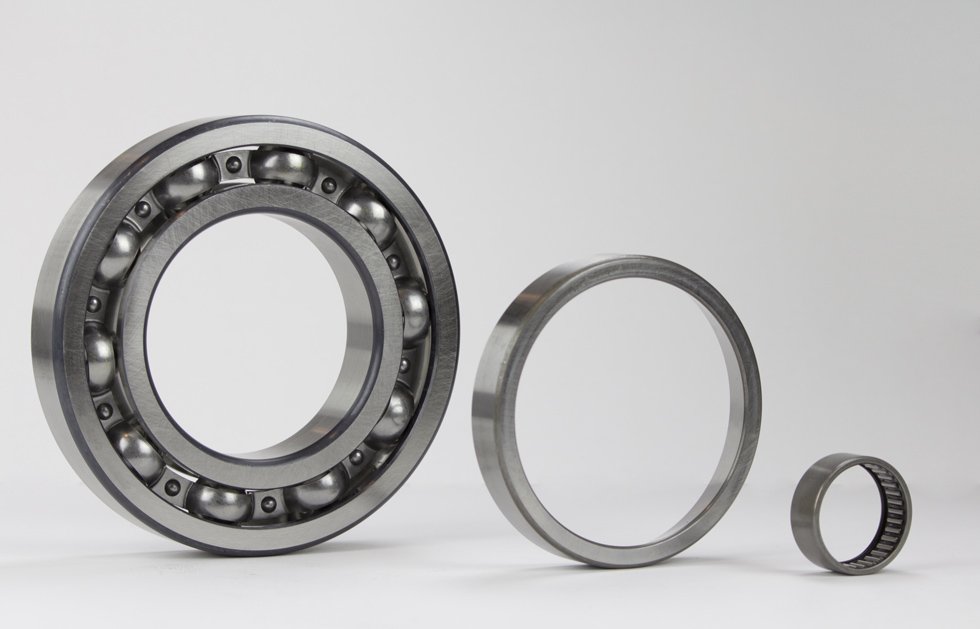
Ball Bearings
Ball bearings reduce friction between shafts and axles and carry radial loads, thrust loads, or a combination of both. They contain an outer ring, inner ring, and a cage that holds and spaces bearing balls, the bearing’s spherical rolling elements. These bearing balls must be perfectly rounded and spaced to prevent friction and bearing failure.
Ball bearings come in single- and double-row configurations depending on the type and direction of loads they carry. There are many types of ball bearings. Ball thrust bearings only carry axial loads, while angular contact ball bearings support both thrust and radial loads. The radial load an angular contact ball bearing can support is directly proportionate to the axial load it can support. Self-aligning ball bearings compensate for improper bearing mounting that leads to misalignment. Thin-section ball bearings are used in small spaces that have weight restrictions.

Roller Bearings
Roller bearings are a type of bearing that use rolling elements to support loads and reduce friction. As opposed to ball bearings, roller bearings have barrel-shaped rolling elements instead of spherical balls. They are capable of supporting heavier loads than similarly sized ball bearings but cannot handle as high of speeds as ball bearings.
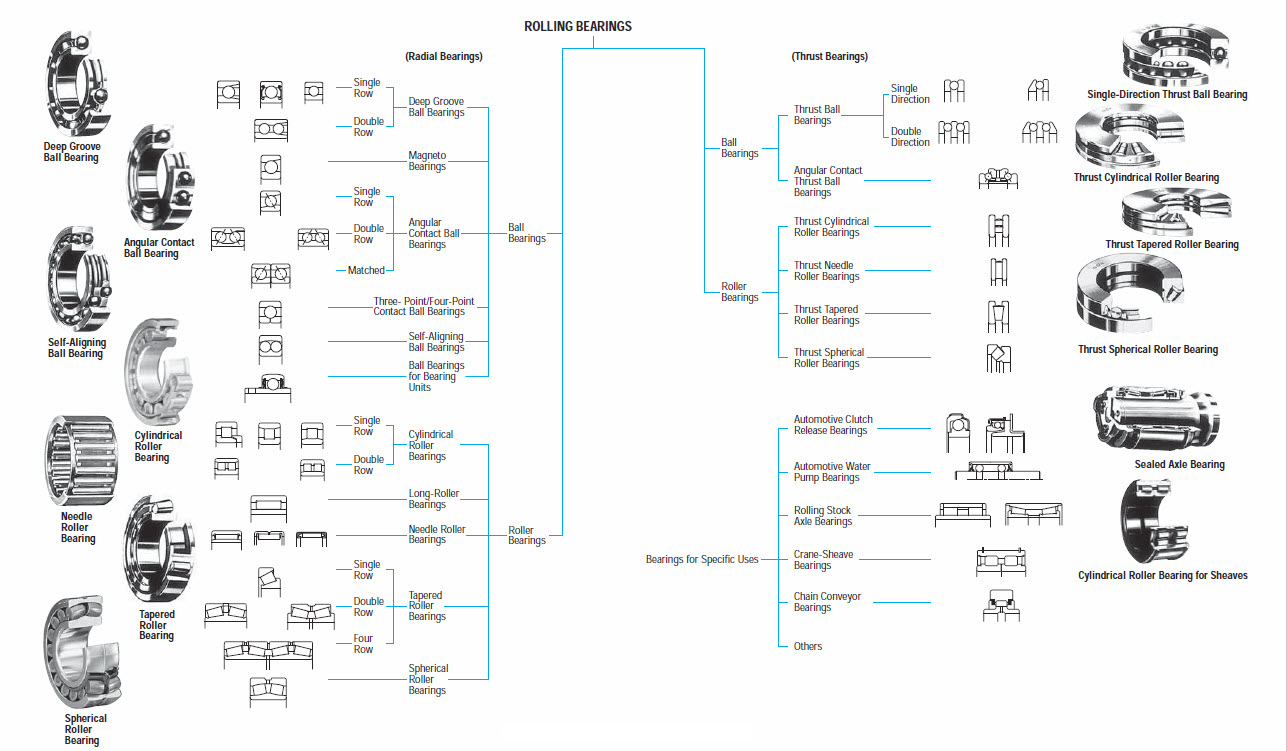
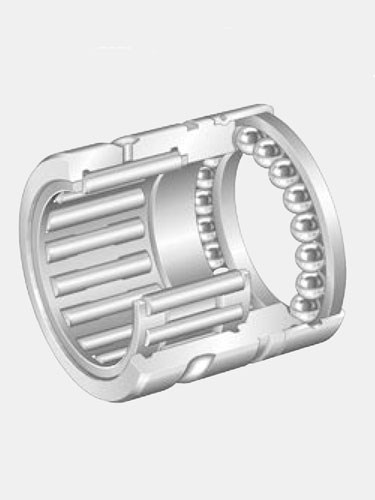
Roller bearings contain an inner and outer ring that house the rollers and bearing cage. Also known as a retainer or separator, the cage maintains spacing between rollers and holds the bearing together. There are a wide range of roller bearings, each with different designs used in varying applications. Cylindrical, spherical, tapered, and needle are the four primary types of roller bearings.
Cylindrical roller bearings handle high radial loads and low thrust loads at high speeds. They also accommodate fast acceleration. Spherical roller bearings contain two rings on the inner raceway to handle a variety of loads and misalignment concerns. The rollers share a single sphered outer ring. With two rows of spherical, barrel-shaped rollers, spherical roller bearings can withstand heavy radial loads and certain axial loads in both directions. They are self-aligning to handle shaft misalignment and mounting problems. Tapered roller bearings contain tapered inner and outer raceways and rollers to accommodate simultaneous radial and thrust loads. Providing true rolling motion and low friction, tapered roller bearings are ideal for supporting heavy combined loads. Needle roller bearings use long, thin cylindrical rollers to support radial loads. Featuring a thinner cross section than other roller bearings, needle roller bearings are ideal in situations that require high load-carrying capacities within a limited space.

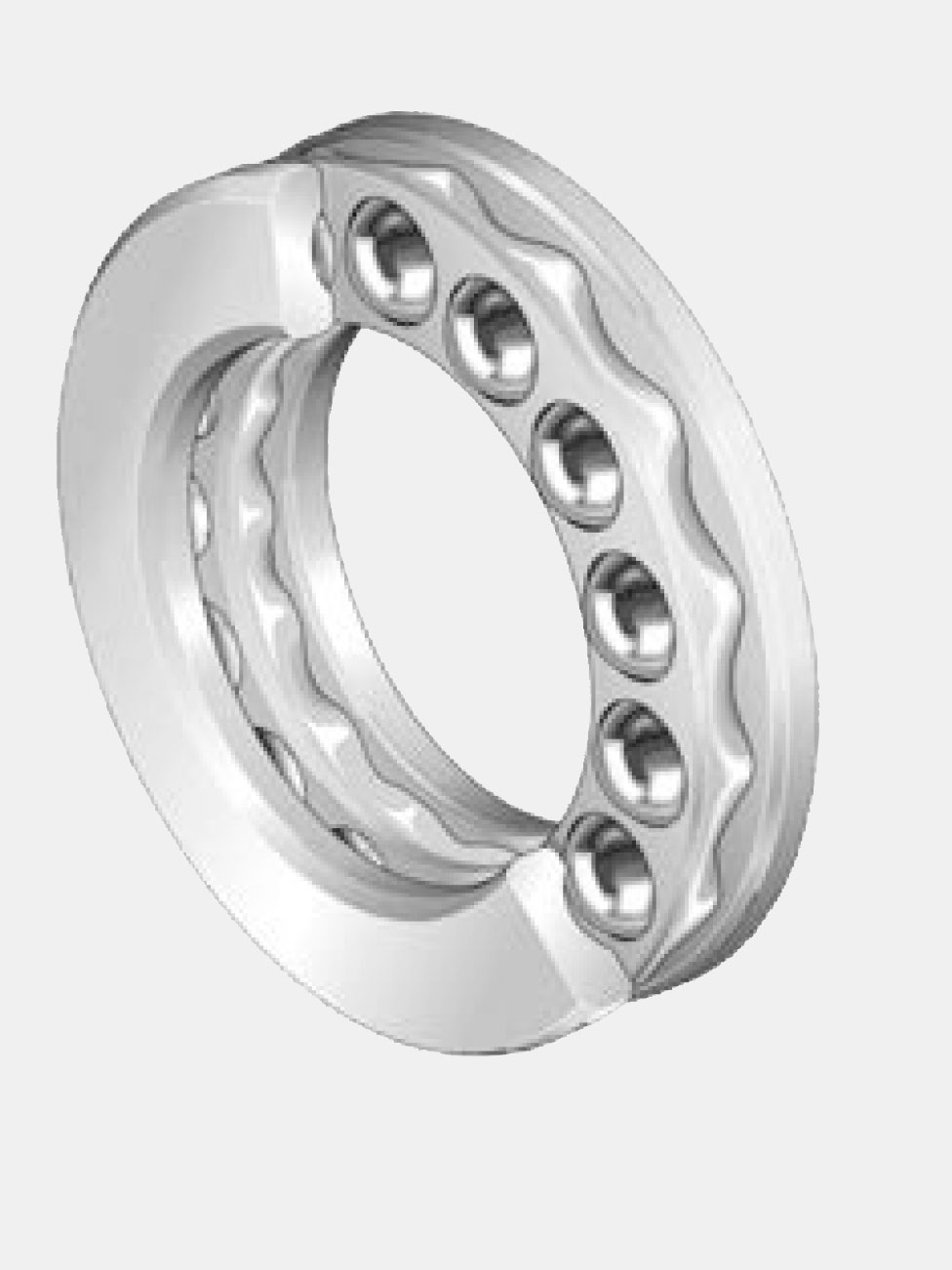
Thrust Bearings
Thrust bearings include a broad range of bearings that accommodate axial loads. Also referred to as axial force, thrust is parallel to the axis of rotation. Depending on the application, there are many types and variations of thrust bearings.
Ball thrust bearings effectively withstand pure thrust loads. The two rings, also called washers or washer seats, often feature grooves to allow for higher load capacities. Ball thrust bearings are available in single- or dual-direction designs. Aligning seat washers correct initial assembly misalignments. Flat-race bearings typically have lower limiting speeds than grooved-race bearings. Hydrodynamic thrust bearings act on pressurized fluid and facilitate motion in a wide range of heavy-duty industrial equipment. Fixed and tilting-pad hydrodynamic thrust bearings may be used in hydroelectric turbines and generators.

Mounted Bearings, Housings & Inserts
Flange-Mount Bearings
Flange-mount bearings support heavy loads when the shaft axis is perpendicular to the mounting surface, which can flex the shaft and create harmful vibration. To stabilize and support the shaft, flange-mount bearings are mounted in one of three flange forms. Four-bolt flange-mount bearings can support the highest loads. They come in a square or circular flange shape. Three-bolt flange-mount bearings support moderate loads and come in a circular form or triangular form offset from the round bearing. Two-bolt flange-mount bearings, which offer the least support, come in a diamond shape.
Flange-mount bearings also use different types of bearings for different applications. Roller bearings offer higher load support, ball bearings decrease friction and operate at faster speeds, and plain bearings control the shaft’s linear movement.
Hanger Bearings
Hanger bearings provide adjustable support in high-vibration conditions such as screw conveyors. They consist of a bearing mounted in a round housing. This housing has either a threaded boss used to vertically mount the housing or a fixed swivel to align the bearing with the shaft. To prevent loose bearings, bearings may be locked into the housing with a collar and setscrew. Roller bearings, which operate with less friction and vibration than plain bearings, may also have felt seals that seal in lubricant, keep out contaminants, and increase bearing longevity.
Insert Bearings & Cartridges
Insert bearings are easily mounted bearings that reduce friction and carry loads. They have inner diameters larger than the shaft on which they are installed and do not need to be press-fit onto shafts like standard bearings. They require setscrews, locking collars, and tapered adapters to secure their position. Insert bearings used in high-speed applications can be relubricated through an oil hole in the outer ring, and bearings used in food processing can be coated in black oxide to resist corrosion.
Mounted Hydrodynamic Bearings
Mounted hydrodynamic bearings carry loads and support shafts but do not have rolling elements. Also called fluid dynamic bearings, they use a layer of water or oil continuously drawn in by their own motion to reduce friction and carry many tons of weight. Hydrodynamic bearings use a pump to start and stop because dry startups quickly wear down bearings. They are used only in environments with little shock or vibration because shock can disrupt the fluid film and cause the bearing to fail. In an ideal environment, hydrodynamic bearings operate at high speeds and temperatures without wear.
Mounted Wheel Hub Units & Integrated Assemblies
Mounted wheel hub units and integrated assemblies combine bearings, housings, and lubricant into one easily installed unit. Integrated assemblies improve function and safety in medical equipment, wheels, transmissions, and steering systems. They also reduce vehicle maintenance and improve brake performance. Wheel hub units are easily mounted and maintained. They have an outer flange to fix the unit to a vehicle’s suspension and an inner flange to fix the unit to the brake. Wheel hubs often use tapered bearings to carry radial and axial loads.
Pillow Block & Base-Mount Bearings
Pillow block and base-mount bearings carry radial and axial loads. They are often mounted in housings called pillow blocks, which support shafts and increase precision. The pillow block protects the bearing and contains the mounting holes while setscrews or locking collars secure the insert bearing in the pillow block. Pillow blocks compensate for mounting errors and may be split into two pieces to easily inspect and replace bearings.
Take-Up Bearings & Frames
Take-up bearings and frames align conveyor tracks and adjust and maintain tension on conveyor belts. These assemblies contain a bearing, housing, guiding frame, and positioning screw. The positioning screw adjusts the bearing and housing’s location along the frame. This frame must be long enough to achieve proper tension in the belt. Take-up frames can be center-pull, top-pull, or bottom-pull depending on the positioning screw’s location in the assembly. Frames guide the take-up bearing while the bearing reduces friction.















 It is a company with more than 45 years of experience selling and exporting bearings, belts, chains and seals to US Central America, South America and the Caribbean Islands.
It is a company with more than 45 years of experience selling and exporting bearings, belts, chains and seals to US Central America, South America and the Caribbean Islands.